Note: Azure search is currently in preview (at the time of writing), you might need to request access first using your Azure subscription in order to view/use this functionality. To test this service, you can use one of the free packages.
What is Azure Search
Azure search is an indexing service where you can look for content in documents. You could compare it with your personal Bing search engine for your own indexed documents. You can configure and search your documents by using the Azure Search REST API.
Typical usage flow:
- Create an Azure Search Service using the portal
- Create an Index schema
- Upload documents to the index
- Query the Azure Search for results
Configuring Azure Search Service using the the preview portal
In order to start using Azure Search, you will need:
- Your own namespace URL. (eg. https://coditshared.search.windows.net)
- Administration API key. (used for configuration)
- Query API key. (for retrieving results)
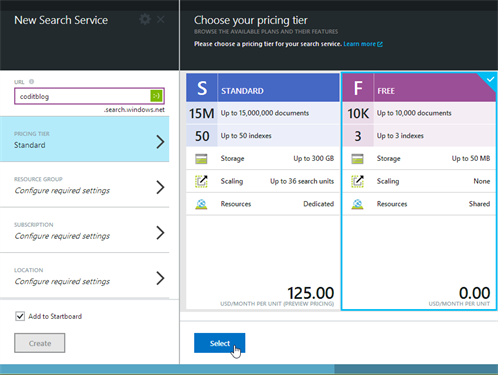
Creating the search service
Browse to https://portal.azure.com and follow the instructions as shown in the following screenshots.
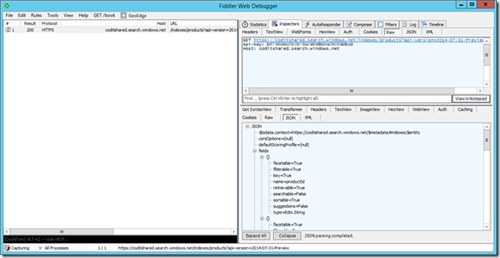
Using Fiddler to configure your search
Once you have set up your Azure Search Service, we can start using the API. You might notice the api-version query url parameter that you might need to change as things evolve.
Creating an index
POST Example
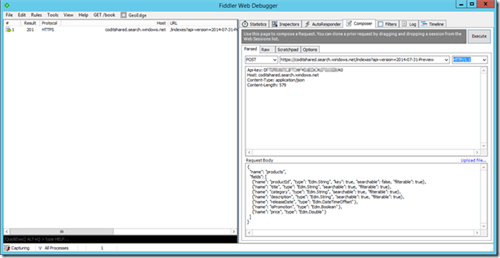
POST https://coditshared.search.windows.net/indexes?api-version=2014-07-31-Preview HTTP/1.1
Api-key: DXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX0
Host: coditshared.search.windows.net
Content-Type: application/json
Content-Length: 579
{
"name": "products",
"fields": [
{"name": "productId", "type": "Edm.String", "key": true, "searchable": false, "filterable": true},
{"name": "title", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true},
{"name": "category", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true},
{"name": "description", "type": "Edm.String", "searchable": true, "filterable": true},
{"name": "releaseDate", "type": "Edm.DateTimeOffset" },
{"name": "isPromotion", "type": "Edm.Boolean" },
{"name": "price", "type": "Edm.Double" }
]
}
Modifying your index
Deleting your index
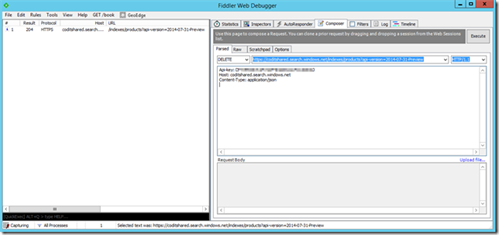
DELETE https://coditshared.search.windows.net/indexes/products?api-version=2014-07-31-Preview HTTP/1.1 Api-key: DXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX0Host: coditshared.search.windows.net
You should receive a 204 No Content response.
Retrieving existing indexes configured on your Azure Search Service
GET https://coditshared.search.windows.net/indexes/products?api-version=2014-07-31-Preview HTTP/1.1 Api-key: DXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX0 Host: coditshared.search.windows.net
Index new blob files
We previously created a new Azure Search index. It’s time to populate the index with some documents. For each document you need to upload it to the Search Service API as JSON format using the following structure:
{
"value": [
{
"@search.action": "upload (default) | merge | delete",
"key_field_name": "unique_key_of_document", (key/value pair for key field from index schema)
"field_name": field_value (key/value pairs matching index schema)
...
},
...
]
}
Hands-on: Index new blob files using Azure WebJobs
Because “we” (developers) are lazy and try to automate as much as possible, we could use Azure WebJobs as a blob polling service and then index each new blob file on the fly. For the sake of simplicity, we will only send 1 file to the Azure Search API service, you could however send over a batch to the indexing service (~ max 1000 documents at once and size should be < 16MB).
The following example is available for download on Github
Creating the Azure WebJob
More information on how to create a WebJob can be found here
Creating a WebJob is fairly easy, you just need to have the following static method to pickup new blob messages:
public static void ProcessAzureSearchBlob([BlobTrigger("azure-search-files/{name}")] TextReader inputReader) { }
B00FFJ0HUE
ASUS EeePC 1016PXW 11-Inch Netbook
Computers Tablets
Graphics: Intel HD Graphics Gen7 4EU
Cameras: 1.2MP
Operating System: Windows 8.1
2013-11-12T00:00:01.001Z
false
362.90
var deserializer = new XmlSerializer(typeof(Product), new XmlRootAttribute("Product"));
var product = (Product)deserializer.Deserialize(inputReader);
inputReader.Close();
var jsonString = JsonConvert.SerializeObject(product,Formatting.Indented, new JsonSerializerSettings { ContractResolver = new CamelCasePropertyNamesContractResolver() });
message.Content = JObject.Parse(jsonString);
var indexObject = new JObject();
var indexObjectArray = new JArray();
var itemChild = new JObject { { "@search.action", "upload" } };
itemChild.Merge(message.Content);
indexObjectArray.Add(itemChild);
indexObject.Add("value", indexObjectArray);
POST https://coditshared.search.windows.net/indexes/products/docs/index?api-version=2014-07-31-Preview HTTP/1.1
api-key: DXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX0
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
Host: coditshared.search.windows.net
Content-Length: 431
{
"value": [
{
"@search.action": "upload",
"productId": "B00FFJ0HUE",
"title": "ASUS EeePC 1016PXW 11-Inch Netbook",
"category": "Computers \ Tablets",
"description": "n Graphics: Intel HD Graphics Gen7 4EUn Cameras: 1.2MPn Operating System: Windows 8.1n ",
"releaseDate": "2013-11-12T00:00:01.001Z",
"isPromotion": false,
"price": 362.9
}
]
}
And the response:
HTTP/1.1 200 OK
Cache-Control: no-cache
Pragma: no-cache
Content-Type: application/json; odata.metadata=minimal
Expires: -1
request-id: 1abe3320-de0e-47aa-ac65-c6aa15f303c3
elapsed-time: 15
OData-Version: 4.0
Preference-Applied: odata.include-annotations="*"
Date: Thu, 21 Aug 2014 07:20:29 GMT
Content-Length: 221
{"@odata.context":"https://coditshared.search.windows.net/indexes('products')/$metadata#Collection(Microsoft.Azure.Search.V2014_07_31_Preview.IndexResult)","value":[{"key":"B00FFJ0HUE","status":true,"errorMessage":null}]}
To make things easy, I’ve created a test client that sends the message to blob for you.
Querying the Azure Search Service
Querying is done using the Query API Key.
Lookup
You can do a simple lookup by the key of your index schema. Here we can lookup the previously uploaded document with productId: B00FFJ0HUE
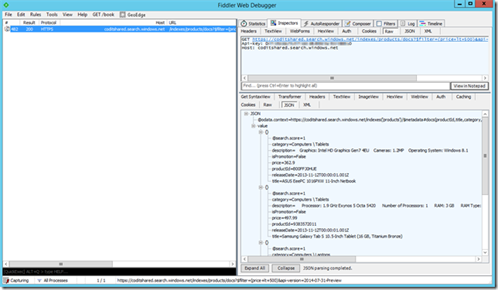
GET https://coditshared.search.windows.net/indexes/products/docs/B00FFJ0HUE?api-version=2014-07-31-Preview HTTP/1.1 Api-key: DXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX0 Host: coditshared.search.windows.net
Simple query syntax
Querying is fairly simple. For a complete overview, you should check the complete API reference. For this example, the service has 5 product documents. 4 of them have a price lower than 500. We can execute the following query to retrieve the 4 products.
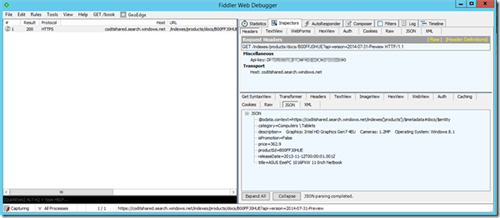
GET https://coditshared.search.windows.net/indexes/products/docs?$filter=(price+lt+500)&api-version=2014-07-31-Preview HTTP/1.1 Api-key: DXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXXX0 Host: coditshared.search.windows.net
Azure Search also supports paging, so we can also $skip and $take a number of results.
More info on the syntax to create specific queries: MSDN
Additionally the following characters may be used to fine-tune the query:
- +: AND operator. E.g. wifi+luxury will search for documents containing both “wifi” and “luxury”
- |: OR operator. E.g. wifi|luxury will search for documents containing either “wifi” or “luxury” or both
- -: NOT operator. E.g. wifi -luxury will search for documents that have the “wifi” term and/or do not have “luxury” (and/or is controlled by searchMode)
- *: suffix operator. E.g. lux* will search for documents that have a term that starts with “lux”, ignoring case.
- “: phrase search operator. E.g. while Roach Motel would search for documents containing Roach and/or Motel anywhere in any order, “Roach Motel” will only match documents that contains that whole phrase together and in that order (text analysis still applies).
- ( ): precedence operator. E.g. motel+(wifi|luxury) will search for documents containing the “motel” term and either “wifi” or “luxury” (or both).
There is more than this…
Time to mention some extra features that are out of scope for this blogpost:
CORS Support
When using javascript to query the service, you will expose your API Query key to the end-user. If you have a public website, someone might just steal your key to use on their own website. CORS will prevent this by checking the HTTP Headers where the original request came from.
Hit highlighting
You could issue a search and get a fragment of the document where the keyword is highlighted. The Search API will respond with HTML markup (<em />).
Suggestions
Provides the ability to retrieve suggestions based on partial search input. Typically used in search boxes to provide type-ahead suggestions as users are entering text. More info: MSDN
Scoring Profiles
Scores matching documents at query time to position them higher / lower in ranking. More info: MSDN
Performance and pricing
When you are interested for using the service in production, you can pay for a dedicated Search Unit. Search Units allow for scaling of QPS (Queries per second), Document Count, Document Size and High Availability. You could also use Replicas in order to load balance your documents.
And more…
Download Sample
Sample code can be found here: https://github.com/jvanderbiest/Codit.AzureSearch.Sample
Subscribe to our RSS feed